Risk Management
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is the Group's structure that supports management in identifying, assessing and monitoring risks, as well as defining the most effective response strategies for their mitigation.
The approach adopted by ERM is based on the principles envisaged by the Enterprise Risk Management – Integrated Framework, international standard issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO Report).
Risk management is an annual basis process that involves both the entire Corporate perimeter and a plurality of corporate functions.
The Risk Management Model is characterized by a structured approach, based on international best practices and considering the guidelines of the Internal Control and Risk Management System, which is structured on three control levels:
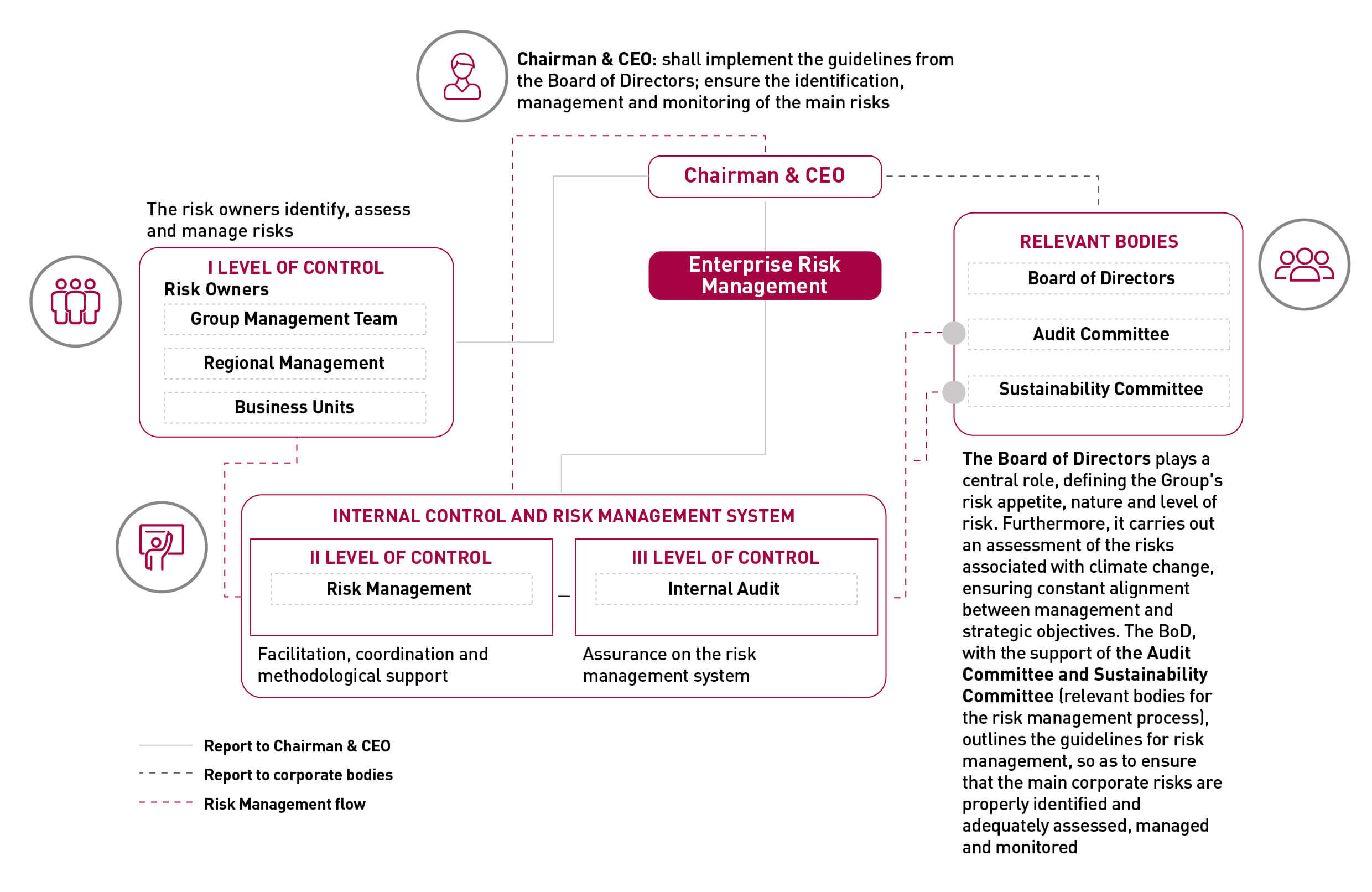
The Risk management process takes a top-down and risk-based approach, starting from the definition of Cementir's Industrial Plan. It ensures that major risks are identified, assessed, managed and monitored while taking into account the individual operations, risk profiles and risk management systems of each business unit, to create a wholly integrated risk management process. Risks are assessed with quantitative and qualitative tools considering both the probability of occurrence and the impacts that would be generated in a given time horizon if the risk were to occur. It also ensures that all necessary measures are taken to control risks that could threaten the Group's assets, its ability to generate profits or achieve its objectives.
At an operational level, the risk owners, through the support of the Risk Management function, identify the risks under their responsibility and provide an indication of the actions necessary to mitigate them. The results of this activity are subsequently consolidated in order to identify risks at the Group level, allowing an integrated management.
Risks are defined in a "Risk Library" divided into five macro categories:
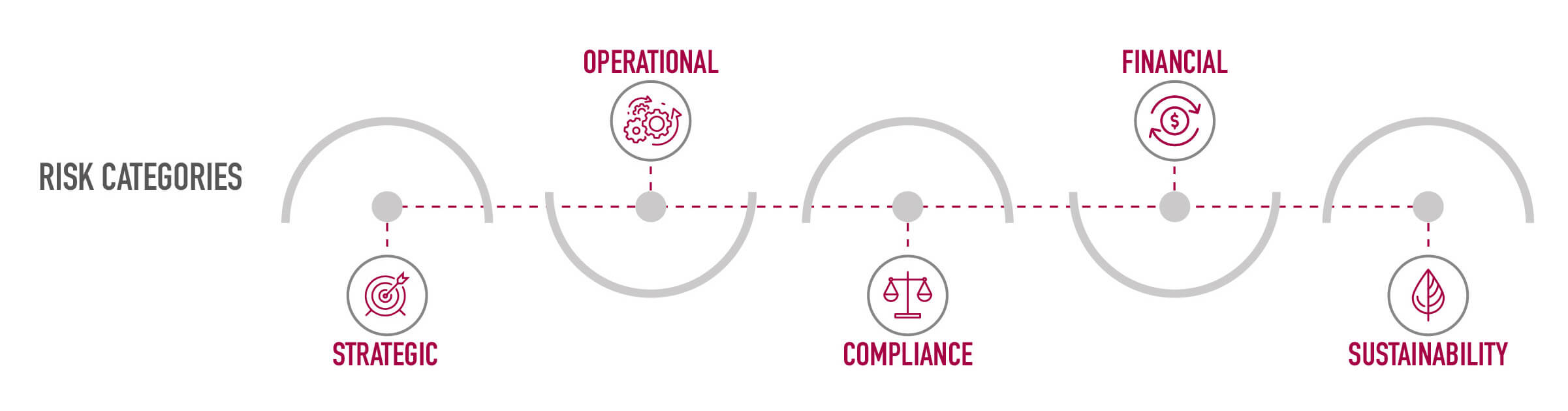
This library is updated periodically: the latest update has included specific risks on climate change issues.
The Cementir Group's Internal Control and Risk Management System is integrated with the Group's Sustainability Strategy. Starting from 2021 the Cementir Group has launched a project to implement the recommendations of the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosure) committing to be transparent on risks and opportunities related to climate change. The identification, assessment and effective management of risks and opportunities related to climate change are fully integrated into the Group's risk management process. To promote and improve its climate change disclosure, in 2022, the Group engaged Standard & Poor's (S&P) to assess physical and transitional climate risks and develop scenario analyses to support the implementation of the TCFD guidelines. The analysis carried out by S&P showed that the Cementir Group scored 100% on the overall assessment of the eleven recommendations of the TCFD, which represents a complete and transparent level of disclosure achieved. Furthermore, the Group is integrating the guidelines published by the European Union “EU Taxonomy Regulation”, which together with the TCFD constitute the reference frameworks.
MAIN RISKS TO WHICH THE GROUP IS EXPOSED
The main types of risks and opportunities to which the Group is exposed are described below.
STRATEGIC RISKS
-
Uncertain outlook
Description Impact Mitigation actions The results of the business activities are highly dependent on the economic conditions of the countries of operation:
- Inflation is projected to decline gradually in 2025 (with the exception of Egypt where it is expected to increase), but is expected to remain above central bank targets in most economies. Overall inflation in world economies is expected to be 4.5% in 2025, with the advanced economies that are expected to return to their inflation targets sooner than emerging market and developing economies.
- Monetary policy will remain cautious until there are clear signs of a sustained reduction in underlying inflationary pressures.
- The slowdown in China's economy poses a significant risk to global output growth.
- Global growth is projected to be 3.3% in 2025. In the US, growth is expected to be 1.6% in 2025, while in Europe it is expected to be around 1.3%, registering modest growth.
Conflicts between Russia and Ukraine, along with those in the Middle East, continue to have a significant impact on the global economic landscape. Simultaneously, the growing rivalry between the United States and China is expected to influence global companies' strategies, particularly in relation to supply chains and markets.
Demand for construction materials is fundamentally driven by economic growth. These changes in demand may affect volumes, selling prices and the structure of the industry.
The Group estimated a potential reduction in sales volumes The Group, with the support of the relevant departments:
- actively monitors market conditions in order to anticipate any adverse scenarios.
- Optimises the product portfolio for growth by increasing profitable low-carbon solutions.
- aims to maintain strict cost discipline and stable prices to ensure a high contribution margin.
- establishes long-term contracts to secure favourable logistics and energy costs.
-
Geopolitical risk
Description Impact Mitigation actions The Group operates on five continents and is exposed to political risks both locally and globally. The geopolitical instability of some of them (e.g. Turkey and Egypt) may influence demand trends.
The ongoing conflict between Israel and Palestine, which has now spread to other states in the Middle East, together with the continuing conflict between Ukraine and Russia, is currently the main factor in international geopolitical instability.
The medium-term outlook remains highly uncertain, with numerous challenges hampering efforts to identify a path towards de-escalation.
Given the strategic locations of the conflicts, the impacts on the global economy are substantial and are expected to result in the following:
- Significant uncertainty for the markets;
- Likely increases in transportation and logistics costs, affecting the Group’s procurement and sales processes;
- Sales bans to sanctioned countries affecting Group’s export volumes;
- An increase in oil prices could slow down the global economy and drive inflation higher;
Heightened social instability.
Impact on the Group's economic/financial results Continuous monitoring of the environment, mainly focused on the critical political/institutional developments and regulatory aspects which can potentially affect the business, but the geographical differentiation helps to limit the exposure to any particular market and currency.
Alternative markets.
FINANCIAL RISK
-
Currency exchange risk
Description Impact Mitigation actions The Group operates with ten different currencies, and fluctuations in exchange rates may impact the Group’s business, operational results, and financial condition. Among these, the Turkish Lira and the Egyptian Pound are the principal currencies influenced by a significant depreciation in the last years.
The Turkish lira is the currency that has depreciated significantly recently, by about 27% since September 2023 (September 2023: €/TRY 28.86 – January 2025: €/TRY 36.70). In March 2024, the Turkish central bank raised the rate to 50% to avoid further devaluation, marking a change of course after two years of monetary easing in which the reference rate had been reduced to 8.5% from 19% in 2021. As of April 2022, the Turkish economy is classified as hyperinflationary, according to the criteria outlined in “IAS 29 - Financial Reporting in Hyperinflationary Economies”.
The Egyptian pound also suffered a significant devaluation, weakening by around 58% since September 2023 (September 2023: €/EGP 33.01 – January 2025: €/EGP 52.29).
These unfavourable changes in the exchange rates used to translate these currencies into the reporting currency have had and will continue to have an impact on the Group’s consolidated results.
Unfavourable exchange rate changes could continue to adversely affect Group profits. The Group continuously monitors currencies in order to seize the opportunities offered by hedging transactions.
To mitigate potential losses, the Group creates a balance between bank accounts in local currency and bank accounts in hard currency.
OPERATIONAL RISKS
-
Talent and retention management
Description Impact Mitigation actions Failure to adequately attract, retain and develop talent could result in the loss of key resources, preventing the Group from executing its strategy. The Group is currently grappling with a labour shortage that is affecting some positions. Difficulty in achieving strategic objectives due to a lack of talent. The Group seeks to attract new talent through specific actions, such as international mobility and career development campaigns, such as the Talent Program initiatives launched in 2022 and the Middle Management Program launched in 2024.
In May 2024, the global "Your Voice" survey was carried out to assess staff engagement across the Group. Compared to the previous edition, there was a 2% increase in employee participation rate compared to the 2022 figures (2024 = 98%) and a 1% increase in employee engagement compared to the 2022 figures (2024 = 58%).
Among the initiatives launched by the Group to mitigate the risk there is also:
- continuing education activities (e.g. Linkedin Learning and the Cementir Academy);
- Specific actions related to internal communication, employer branding and relations with local institutions, schools and universities (e.g. the Concrete programme in Turkey);
- Leadership programme in the Group's main subsidiaries (Aalborg Portland, CCB and Cimentas);
- Constructive relations with unions representing employees: the Group has also updated the collective agreement with the European Working Council for the next four years;
Constant updating of succession plans to ensure business continuity.
-
Health & Safety
Description Impact Mitigation actions The Group's activities operate in a sector that presents inherent health and safety risks, including, for example, driving heavy vehicles, working at height, working in confined spaces, handling live equipment, etc.
Failure to ensure safe workplaces could result in a deterioration in the Group's safety performance and consequent negative regulatory actions or legal liabilities. Health and safety incidents could have a significant impact on the Group's operational and financial performance, as well as its reputation.
Risk of accidents due to unsafe behaviour or conditions, which may cause consequences on the health of workers and/or problems in production processes.
The Group has defined a specific roadmap to 2030, focusing on increasing employee awareness and involvement and strengthening internal procedures and related controls..
Impacts:
• Economic
• Organisational
• Reputational
• Relations with local communities
• Workers’ healthImprovement of the Group's safety culture by sharing best practices and common rules across the Group (e.g. Golden Rules).
Regular risk assessment by all plants to eliminate/mitigate risks (annual action plans).
Group monitoring of H&S performance and effectiveness of corrective measures.
Periodic verification of the effectiveness of the main H&S processes for all plants (e.g. work permits, incident management, etc.).
Variable pay of managers based on H&S indicators and performance.
-
Cybersecurity
Description Impact Mitigation actions The Group increasingly relies on information technology and cloud services to manage and support its operations and relationships with suppliers and customers.
This trend increases a company's exposure to cyber attacks, security breaches, data loss, data theft (including confidential data), also making it more vulnerable to damage caused by uncontrollable events (e.g. power outages, natural disasters, network failures).
In recent years, the frequency, complexity and impact of cyber attacks have increased compared to the past.
The Group is taking prompt action to mitigate and reduce the effects of this risk.
Looking to the future, information technology will play a key role in the Group's strategy, resulting in further exposure to related risks.
- Fraud
- Data loss
- Privacy impacts
- Business interruption
- Reputational damage
- Strengthening of the network infrastructure
- Strengthening of protection systems
- Constant updating of internal procedures
- Continuous training for all staff to strengthen the corporate culture on cyber security issues.
COMPLIANCE RISKS
-
Compliance
Description Impact Mitigation actions These are risks related to compliance with applicable regulations (antitrust, anti-corruption, GDPR, Legislative Decree 231/2001). Potential violations of laws and regulations In relation to these risks, the Legal Department implements targeted programs with guidelines, procedures and training to ensure compliance with the above regulations. The Organisation and Control Models required under Legislative Decree 231/2001 are periodically updated.
The Internal Audit function carries out specific audits on compliance with regulations.
CLIMATE CHANGE
The cement industry's ability to reduce its CO2 emissions and respond to climate change has become a focal point for investors. In 2021, the Cementir Group has launched a project to implement the recommendations of the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosure) committing to be transparent on risks and opportunities related to climate change. Cementir is also committed to ensuring the transparency of its climate-related risks and opportunities in line with the taxonomy required by the European Union. The identification, assessment and effective management of risks and opportunities related to climate change are fully integrated into the Group's risk management process.
As suggested by the TCFD, the Group monitors the risks and opportunities arising from the evolution of transition scenarios and the evolution of physical variables.
Physical variables are divided into two categories of risk:
- Acute: related to the occurrence of extreme weather conditions such as cyclones, hurricanes or floods. Acute physical phenomena, in the various cases, are characterised by considerable intensity and a frequency of occurrence that is not high in the short term, but which, considering long-term scenarios, sees a clear upward trend;
- Chronic: refers to gradual and long-term changes in climate patterns (e.g., sustained high temperatures) that can cause sea-level rises or chronic heat waves.
With regard to the energy transition process, towards a progressive reduction of carbon emissions, there are risks and opportunities linked to changes in the regulatory, technological, market and reputational context.
The Group has decided to align itself to the TCFD framework to clearly represent the types of risks and opportunities by indicating how each of them should be managed. The effects were assessed over three time horizons: the short term (1-3 years), linked to the implementation of the Industrial Plan; the medium term until 2030, in which it will be possible to see the effects of the energy transition; the long term until 2050, by which the Group is committed to achieving net-zero emissions throughout its value chain. As the TCFD states, the process of disclosing risks and opportunities related to climate change will be gradual and incremental from year to year.
-
Chronic and acute physical phenomena
The Group’s plants are located in locations with overall moderate levels of physical risk over the time horizon to 2050, as shown in the following table.
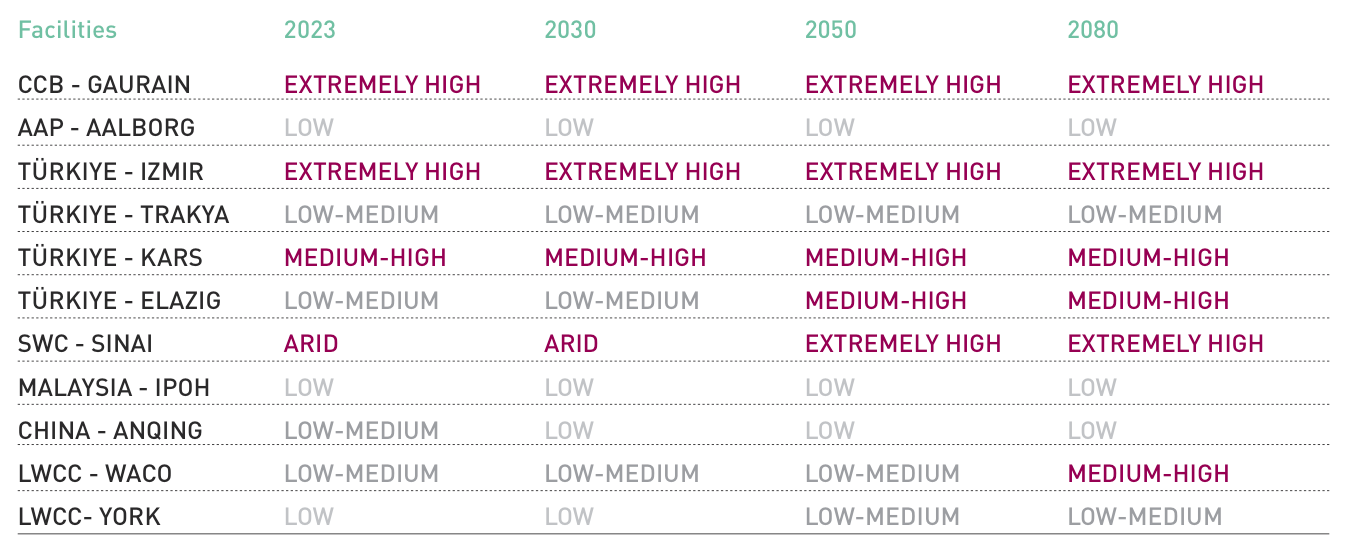
Strategically, the Group’s geographical diversification provides a high degree of resilience. The Group adopts business continuity management processes that ensure an adequate level of maintenance in order to limit and/or reduce damage to corporate assets and ensures the resilience of the business and the restoration of operations in the event of force majeure events.
In some areas (Belgium, Türkiye, Egypt) there is also significant exposure to water stress.
PHISICAL RISK - CHRONIC RISK Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Medium Term Water stress due to global warming The Group operates in certain areas defined as under high water stress, with the risk of increased supply costs. As part of its climate commitments, the Group has defined its policy on water management. Maximising its reuse/recycling, minimising withdrawals and consumption (including losses) and the implementation of efficient operating practices are the main areas of intervention, starting with those geographical areas with the greatest water scarcity.
The Group has set targets to improve specific water consumption in cement production (water consumption (litres) / TCE (ton of cement equivalent)).
In 2024, the targets were updated and now call for a 30% reduction in specific water consumption by 2030, compared to the 2019 value (previously the targets called for a 25% reduction). The target to reduce specific water consumption in high water stress areas remains unchanged at 25 per cent by 2030, compared to the 2019 value.
In addition, the Group is committed to maximising water reuse and recycling, minimising water withdrawals and consumption (including leakage) and implementing efficient operating practices, with a priority for regions facing the most severe water stress.
In 2022, by becoming a signatory to the WASH Pledge, the Group committed to ensuring access to WASH (water, sanitation and sanitation) at an appropriate level of standard for all employees and contractors at all locations under direct control, supporting partners across value chains and communities. Compliance and progress of WASH action plans are monitored periodically.



-
Transition risks and related opportunities
In recent years, the whole Group has been actively engaged in pursuing a transition to a low-carbon economy by defining a 10-year Roadmap. Related risks and opportunities are presented in the following table:
TECHNOLOGY Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Medium – Long Term RISK / OPPORTUNITY
Carbon Capture “CCS”
Technology is the main driver to significantly reduce the company's CO2 emissions in the medium to long term. The adoption of breakthrough technologies is essential to achieve 'net zero emissions' cement production.
The Company places emphasis on the development and implementation of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology as a key component in achieving its CO2 emission reduction targets. Currently, the Group is exploring various opportunities, mainly in Denmark and Belgium.
In October 2024, the carbon capture and storage project developed by Aalborg Portland and Air Liquide was selected by the European Commission to receive a EUR 220 million contribution under the EU Innovation Fund.
The project, which is scheduled to be operational by the end of 2028, will reduce emissions from Aalborg Portland by approximately 1.5 million tons per year.
Previously, Aalborg Portland's target was to capture at least 400,000 tons of CO2 per year, thereby contributing to both the company's emission reduction targets and the Danish government's objectives to reduce Denmark's greenhouse gas emissions by 70% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
The know-how acquired by the Group in this area can be used to develop a carbon capture and storage system at its Belgian subsidiary, CCB, from 2032.
The successful implementation of this innovative technology also depends on exogenous factors outside the company's control, such as CO2 transport and storage infrastructure, public acceptance and climate regulations, which could directly influence and potentially delay the project.
Additionally, a direct risk associated with this new technology is its performance, as no facility to date has successfully operated it worldwide. If the technology does not function as expected, it could compromise the planned CO2 reductions.
Continued support for research and innovation for the development of CCS and the use of CAPEX/OPEX for the full industrialisation of these technologies.
Group involvement in various research projects aimed at facilitating the implementation of carbon capture and storage (CCS) in its operations, including through the installation of pilot plants.


REPUTATION Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Short Term RISK
Reputational risk
According to the Global Cement and Concrete Association, the cement industry is responsible for about 7% of global CO2 emissions. The risk of being perceived as a major carbon emitter by the public could reduce the company's attractiveness to stakeholders.
This reputational risk is further amplified by stakeholders' growing focus on the achievement and consistency of the Group’s climate targets, as well as heightened attention on green claims, especially in light of the new European legislation on the matter.
Cementir is committed to ensuring that its targets are always aligned with the latest scientific developments.
In this regard, in February 2024, the Group received validation of its short- and long-term climate targets by the Science Based Target initiative (SBTi), which confirmed their consistency with the 1.5°C scenario. In addition, SBTi approved Cementir's overall net zero emissions target by 2050.
Cementir is actively engaged with ESG rating agencies to ensure accurate assessment and transparent communication with stakeholders.


POLICY & REGULATION Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Long Term RISK/
OPPORTUNITY
Introduction of new CO2 emission laws and regulations
Following the Paris Climate Agreement (COP21), signatory countries are required to commit to an emission reduction path. It is expected that this will lead to increased regulations, thereby increasing the costs associated with CO2 emissions.
Carbon prices linked to emissions trading systems (e.g., ETS), carbon taxes, and other restrictive policies are expected to increase in the future as governments implement measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in line with the Paris Agreement.
The speed and magnitude of the potential increase in carbon prices due to the new regulations is uncertain and will vary from country to country.
This risk was assessed through different price scenarios (high, medium and low) based on carbon price projections in each country, taking into account the introduction of carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology from 2030.
At the same time, the transition to a decarbonised economy, driven by new standards and regulations, could increase the Group's demand for low-carbon products.
The Group minimises its exposure to the risk of new taxes and regulations by:
- implementing its Roadmap for Sustainability, which aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050;
- developing low-carbon products that meet the requirements of the new regulations;
- maintaining a constant dialogue with national and international bodies.


POLICY & REGULATION Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Medium Term RISK
OPPORTUNITY
CBAM – Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism and ETS reports
If initiatives such as the 'Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism' (CBAM) are not sufficiently designed to protect EU competitiveness, the cement business could face price pressure due to imports from regions with less stringent CO2 regulations. On the contrary, the introduction of this tax could create a competitive advantage over other non-EU cement companies in terms of price. In recent years, the quantities of cement imported into Europe have increased compared to the past. Monitoring the evolution of regulations with the support of international bodies (European Union, Governmental Authorities, Cembureau, GCCA) and consequent transposition to the new rules.
The Industrial Roadmap will support the Group in becoming a resilient company through a low-carbon economy.
In 2024, a Group-wide CBAM procedure was issued.



MARKET Time horizon Description Impact Mitigations action SDG's Medium Term RISK
Scarcity of raw materials
The supply of alternative raw materials, such as fly ash and blast furnace slag, has become increasingly critical due to declining steel production and the gradual closure of coal-fired plants. In the medium term, the phasing out of coal-fired power plants in Europe could lead to a fly ash shortage. At the same time, global demand for these materials continues to grow, making it more difficult to secure long-term contracts and increasing the potential risk of supply shortages.
Another strategic material for the achievement of the Group's objectives is calcined clay, which is essential for the production of FUTURECEM and for the reduction of the clinker ratio. Today, there are a limited number of suppliers. With the development of low-carbon products, the demand for these materials will grow, making the Group more dependent on their prices and availability.
In order to reduce the shortage of these materials, the Group is securing its supply through long-term contracts; search for new suppliers and partial replacement of fly ash with similar materials available on the market (e.g. oxytone).
Another strategy implemented is to secure clay quarries for the production of FUTURECEM.


MARKET Time horizon Description Impact Mitigations action SDG's Medium Term RISK
Biomass shortage
Biomass plays a strategic role in implementing the Group's Sustainability Roadmap and ensuring compliance with European emission regulations.
In the medium to long term, the increasing demand for high-quality biomass could cause supply difficulties and price increases.
In addition, the use of biomass in the Group's plants will require local investments for improvements and/or modifications of the facilities, which are necessary to increase their use.
In order to reduce the shortage of these fuels, the Group is securing its supply through long-term contracts. 

MARKET Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Short term OPPORTUNITY
Development of low emission impact
products
Innovation is a key factor in the long-term success of the company developing low-carbon products. To meet market demands, the Cementir Group has developed new types of cement, such as FUTURECEM, which reduce CO2 emissions by 30% compared to traditional cement, and D-Carb, which reduces the CO2 footprint by 15% compared to traditional white cement.
The Group is also promoting a more environmentally friendly ready-mixed concrete (RMC) offering along the entire value chain and has introduced a new product portfolio under the C-Green and UNI Green brands with a low carbon footprint.
The Group meets the needs of customers along the value chain by developing and delivering products, solutions and technologies that address the key challenges facing the construction industry.
The Group continuously develops and introduces new low emission products: increasing the use of decarbonised material (e.g. blast furnace slag); producing limestone cement or cement using fly ash;
In addition, the Group aims to reduce the clinker ratio by using FUTURECEM and other new products.



RESOURCE EFFICIENCY Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Medium term OPPORTUNITY
Recovery potabilization of water removed in quarry operations
The recovery and potabilization of the water removed during the exploitation of the limestone quarries in Belgium (Clypot and Gaurain) represents an opportunity, because it allows local communities to save the aquifer in an area of high-water stress and allocate it to civil uses.
This recovery increases the company's resilience to future regulatory changes, reduces the risk of conflicts with other stakeholders using the same aquifer (e.g., villagers, customers), and contributes to the sustainable management of water resources.
In Clypot, the entire system has been operational since March 2021, and in 2023, 1,300 megalitres of drinking water were successfully recovered, treated and distributed.
As for the Gaurain quarry, an agreement was signed in 2022 with the local authority to carry out a similar water purification project, with the first investments planned for 2024.
Upon completion of the Gaurain project, an additional 2,000 megalitres of water per year can be recovered, further contributing to sustainable water management and community supply.
Increased water supplies up to 4,000,000 cubic metres per year thanks to investments made in Clypot and Gaurain.
Close collaboration with local authorities to minimise the company's impact on the local community, located in a water-stressed area.




ENERGY SOURCE Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Medium – Long Term OPPORTUNITY
Green Energy
As part of the Group's strategy to reduce Scope 2 emissions, it is planned to increase electricity from renewable sources, either by purchasing or producing it internally. The Group is assessing the feasibility of wind turbine and solar panel projects Definition of a roadmap to increase the use of renewable energy throughout the Group, entering into purchase and/or own production agreements (for example solar panels or wind turbines).
In this regard, in 2023 the Group entered into agreements with Engie and EtherEnergy for its subsidiary in Belgium, CCB, reaching a maximum power that can be delivered, between wind and solar, of 25 MWh.
In Denmark, the government has pledged to obtain 100% of electricity from renewable energy sources by 2030. Aalborg Portland, the Danish subsidiary, is currently in the process of obtaining permits to install two wind turbines.


ENERGY SOURCE Time horizon Description Impact Mitigation actions SDG's Medium term OPPORTUNITY
Increased supply of district heating in the city of Aalborg
The Aalborg plant recovers excess heat from cement production to provide district heating to local residents. In 2023, Aalborg Portland delivered approximately 1 million GJ of energy to the municipality of Aalborg. According to the engineering project developed by the Group, the Aalborg plant could improve energy supply by a further one million GJ reaching 50,000 households. Negotiations are ongoing with the municipality of Aalborg to define the size and increase of the capacity of the heating supply.
The Group is also considering implementing waste heat recovery at its Belgian subsidiary.

